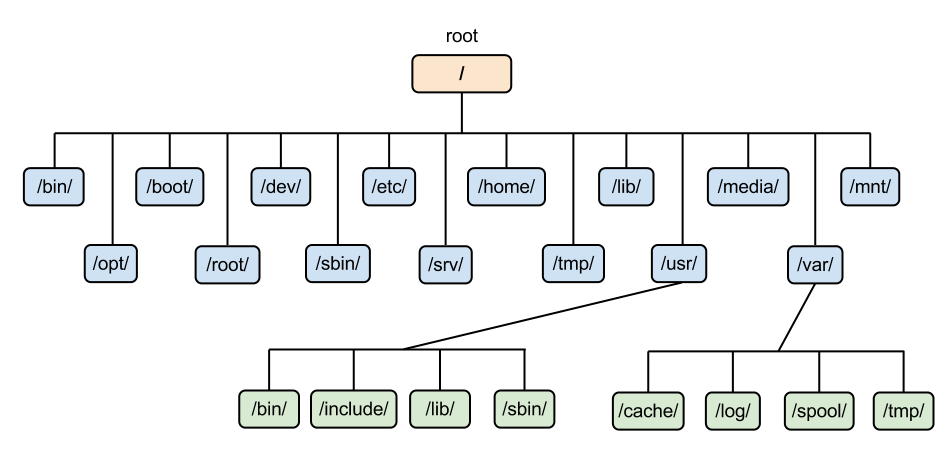
G01
Client Server Architecture
A central server (host computer) serves as both the source
of service requests and the destination for many clients (remote processors) in
a client-server architecture or model of a computer network.
Client computers offer an interface through which a computer
user can ask the server for services and see the results that the server sends
back.
Before responding to client requests, servers wait for them
to arrive.
Client computer requests something from the server. Such as
visiting a website.
Server computer serves the request. Such as responding to
the webpage.
Types of
Client-Server Architecture
1.
1-Tier Architecture
2.
2-Tier Architecture
3.
3-Tier Architecture
1-Tier Architecture
All application-related components are gathered together and
used as a single package to deliver the application in a one-tier client-server
architecture. One entity is made up of all the logic associated with the User
Interface, Business Logic, Database Logic, and Database.
Although a 1-tier architecture is a dependable source due to
its many services, managing it can be challenging.
The main issue is the variance in the data.
Work is frequently repeated.
The presentation layer, business layer, and data layer are
among the layers that make up a 1-tier architecture. These layers are
integrated together via a special software program. Typically, data stored in
this layer is kept on shared drives or local systems.
2 Tier
Architecture
Two layers comprise the entire application logic in a
two-tier client-server architecture.
In this architecture, the database functions primarily as a
separate entity.
Databases are designed independently, and the main
application contains all of the business, database, and user interface logic
needed to interact with the database and process applications. Compared to the
1-tier architecture, this architecture has a better environment.
Since there is no middleman between the client and the
server, 2-tier architectures are faster than 1-tier architectures. Confusion
among clients is reduced thanks to the two-tier architecture. A well-known
illustration of a two-tier architecture is the online reservation system.
3 Tier
Architecture
A 3-tier system's architecture includes a middleware between
the client and the server, in contrast to a 2-tier system's architecture that
lacks one.
The middleware receives requests for information from the
server on behalf of clients. After that, the request will be forwarded to the
server for handling. In the same way, the client will receive a response from
the server.
The presentation layer, application layer, and database
layer are the three primary layers of a three-tier architecture. Every layer
has distinct ends that regulate one another.
The presentation layer is managed by client devices, while
the application and database layers are managed by middleware and servers,
respectively. The three-tier architecture is more secure because of the third
layer's data control functionality, invisible database structures.
Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is the data storage platforms like Google
Drive, Dropbox, OneDrive or Box.
It is the delivery of computing services.
Cloud computing is the Internet-based delivery of various
services.
Data storage, servers, databases, networking, and software
are a few examples of the tools and applications that fall under this category.
With cloud-based storage, files can be saved to a remote
database instead of being stored on a local or proprietary hard drive. An
electronic device can access data and the software needed to run it as long as
it can connect to the internet.
Many factors make cloud computing a popular choice for
individuals and companies, including lower costs, higher productivity, speed
and efficiency, performance, and security.
Cloud
Computing Service model
Unlike a microchip or a cellphone, cloud computing is not a
single technological device. Rather, it is a system that is mainly made up of
three services: infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS), software-as-a-service
(SaaS), and
PaaS, or platform-as-a-service.
IaaS, often known as serverless computing, offers end
users IT infrastructure over the internet.
End users, who are primarily software developers, are served
by PaaS for both software and hardware. The user can create, launch, and manage
their own apps with PaaS without having to worry about building and maintaining
the infrastructure.
SaaS is a type of software licensing that eliminates
the need for local download and installation by enabling software access via
external servers on a subscription basis.