Repeater
- It is a two port devices
- Regenerates the signal without amplifying.
- When signal becomes weak it copies the signal bit by it and regenerate it at the original strength.
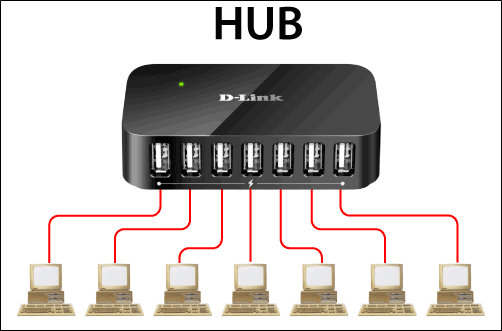
Hub
- Multiport repeater
- Connects multiple wires coming from different branches which means the collision domain of all host connected through Hub remains one.
- Data packets are send to all the connected devices
- Can operate in half-duplex mode
- Types of Hub:
- Active Hub:
- It regenerates signal(clean and boost and relay signal along with the network)
- Serves both as a repeater and a wiring centre.
2. Passive Hub:
- It does not regenerates signal
- It relays signals onto network without cleaning and boosting them
3. Intelligent Hub:
- Works like active hub
- Includes remote management capabilities
- Provides flexible data rates
- Monitors the traffic
Switch
- Multiport bridge with a buffer
- It is a data link layer device
- It can perform error checking
- Data packets are send to the designated device (Intelligent)
- It have different collision hosts but broadcast domain remains same
- Can operate in full-duplex mode
- Some switches have dedicated port for up-linking to another switch
- It works with physical (MAC) address
- It uses switching tables
Router
- Routes data packets based on their IP address
- Mainly a Network Layer Device
- Connects LANs and WANs together
- Different broadcast domains
- Most complex device
- Connects LANs together to create an internetwork- forwards packets from one LAN to another
- It works with logical (IP) address
- It does not forward broadcasts
- Uses routing tables
Note: Network Repeaters and Hubs does not use any interconnecting devices which limits the total cable length and number of connected devices. Repeater resolves such problems.
Multiport Repeater is a several ports to which cables can be connected (aka Hub) which regenerates signal to all ports where computer is connected.
Network Bandwidth is the amount of data transferred in an interval. It is measured in bits per second (bps). Hub shares the amount bandwidth with all connected computers.
Uplink port is used to connect two hubs together or hub to a switch.
Network switches
- Looks like a hub but it sends data packet only to designated port.
- Steps of switch operation:
- Switch receives a frame -Data is end onto medium one frame at a time
- Switch reads the source and destination MAC addresses
- Switch then looks up the destination MAC address in its switching table
- Forwards the frame to the port where the destination MAC can be found
- The switching table is then updated with the source MAC address and port information.
WAP: Wireless Access Point
- Access point (AP) is the heart of wireless network
- All communication passes through the AP
- Wireless LANs are usually attached to wired networks
Network Interface Card
- It mediate the connection between a computer and the networking medium
- It receives bit signals and assembles them into frames, verifies the destination address and removes frame header and sends the resulting packet to the network protocol.
- It receives packets from network protocol and creates frames by adding MAC address
- MAC address is assigned by manufacturer
- NICs support multiple speeds
- Desktop NICs is good enough while Server NICs with onboard memory, multiple ports and performs faster
Promiscuous mode- It turns off the gatekeeper functions and enables the NIC to process all frames it sees. It is used by software called protocol analyser or packet sniffer
- Wireless NICs connect to network using service set identifier (SSID)
Default route: where to send a packet when the router doesn't have an entry in its routing table.
Network unreachable: Message sent when the network can't be found and no default route
Default gateway: In a computer's IP address configuration- the IP address of the computer's router


No comments:
Post a Comment